It is increasingly common to see job offers requesting candidates with knowledge of managing large volumes of data. This is largely due to the rise of Big Data as one of the major trends for the future. And no only for companies that want to adopt a Data Driven strategy, but also for a large number of professionals looking to enter the sector.
You only have to take a look at the main job search portals to see that positions related to Big Data and Artificial Intelligence are the most in demand by companies and head-hunters.
It is often difficult to tell the difference between an analyst, an engineer and a data scientist. All three profiles work with data, but they do so in different ways. Below, we will analyse each of them to know their skills and what are the functions they perform.
What is a Data Engineer and what do they do
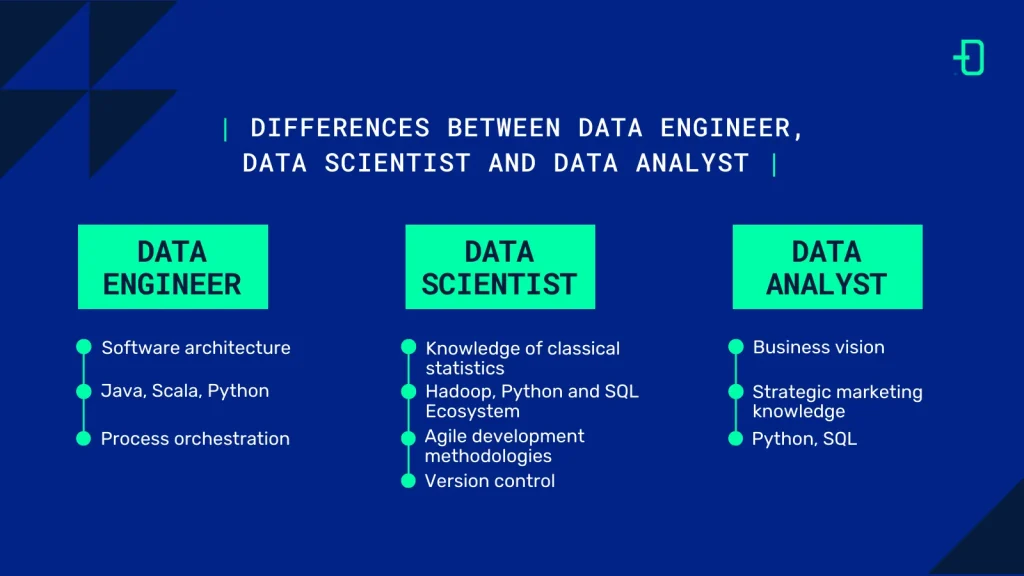
We could define the data engineer as the first link in the chain in the data management process chain. Their main task is to treat, process and transform raw data at source so that it can be subsequently analysed by the data scientist.
Data engineers specialise in process orchestration, database management and software architecture. In addition, they have high knowledge of programming languages such as Java, Scala or Python.
At Damavis, we have a data engineering team that works with technologies ranging from data storage to real-time applications. On the other hand, they are also in charge of building pipelines, automating imports, exports and data transformations through orchestrators.
The profile of the Data Scientist in Big Data
The data scientist is responsible for “translating” the data already treated and processed by the data engineer. Their mission is to convert it into useful information for decision-making in the company.
This profile requires a diverse range of skills, from knowledge of classical statistics and mathematical models, as well as programming languages, including Python and SQL. They also have experience in version control systems, agile development methodologies and notions of the Hadoop ecosystem.
Among other functions, the Damavis data science team is responsible for solving problems of inference, clustering or prediction, through the training of statistical models training. The goal is to develop machine learning-based solutions that convert large datasets into valuable information.
What is a Data Analyst and what do they do
The data analyst is an intermediate figure between the engineer and the data scientist. Their main mission is to participate in the analysis of the data already transformed by the data engineer. Meanwhile, they also gather customer needs and assess the state of the market to transmit this information to the data scientist.
One of the main characteristics of the data analyst is his or her business and marketing vision. For this reason, they must have knowledge of strategic marketing. This enables them to interpret the data and information for the appropriate decision making in the company.
Within companies, the figure of data analysts has become essential and especially in demand in contexts of strategic planning and development of actions.
Evolution of Big Data profiles over time
This post was originally written in 2022. However, it remains relevant today as the fundamental characteristics of profiles have not changed. Nevertheless, we will add this brief update in 2026 to give a glimpse of how they have evolved.
In recent years, we have seen increasingly significant advances in Artificial Intelligence. This is especially true in the field of generative AI, where increasingly powerful models capable of performing incredible feats are emerging.
In this sense, engineering, science, and data analysis will continue to be very secure and prolific professions in the coming years. In addition, the commitment to integrating generative AI tools into the business environment is becoming increasingly common.
Big Data project roles have experienced a major boost and a profound transformation with the maturity of AI.
- Now, data engineers are focusing on real-time data management, automation of the processing stage, and the stability of the AI infrastructure.
- For their part, data scientists are directing their work toward the interpretability of complex models and the integration of AI into business environments.
- As for data analysts, they still need to focus on interpreting insights, monitoring context, and guiding business strategy.
Conclusion
The digitization of processes to deal with the management of the large volumes of data currently handled by companies has become a priority for those organizations seeking to adopt a Data Driven approach or strategy.
Therefore, in the short term, the demand for figures such as engineers, data scientists and analysts will continue to grow, but other types of profiles such as cybersecurity specialists, metatarsal developers or Blockchain technology experts will also be needed.
That is the end of today’s post. If you found it interesting, we encourage you to visit other articles similar to this one in the Damavis category. Don’t forget to share it with all your contacts and give us your opinion on our social networks. See you soon!

